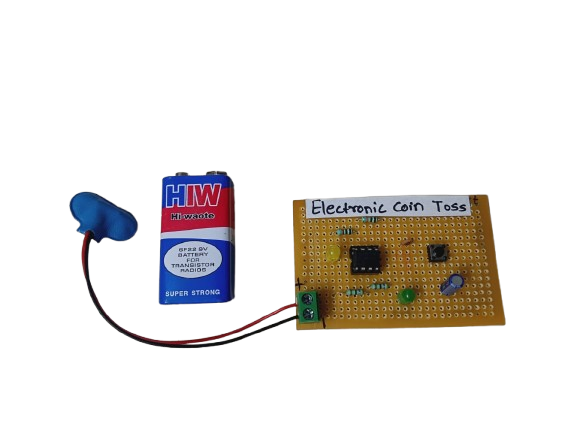
Electronic Coin Toss
₹190.00
In StockThe Electronic Coin Toss is a simple, fun, and educational project that replaces a physical coin with digital logic or microcontroller-based randomness. It’s ideal for learning basic electronics, understanding random number generation, and creating a useful and entertaining tool.
Description
An Electronic Coin Toss circuit is an electronic version of the classic coin flip — often used to make quick decisions, settle disputes, or play games. It mimics the randomness of a real coin toss using digital logic or a microcontroller to generate a pseudo-random result and display it using LEDs or a text display (e.g., “Heads” or “Tails”).
Basic Working Principle:
1.A push-button switch is used to “toss” the coin.
2.Pressing the button triggers a circuit (based on timing or random logic) that rapidly alternates between two states — like a coin flipping.
3.When the button is released, the circuit freezes on either state randomly — representing Heads or Tails.
4.The result is indicated using two LEDs (e.g., Green for Heads, Red for Tails) or a display.
The Electronic Coin Toss is a simple, fun, and educational project that replaces a physical coin with digital logic or microcontroller-based randomness. It’s ideal for learning basic electronics, understanding random number generation, and creating a useful and entertaining tool.