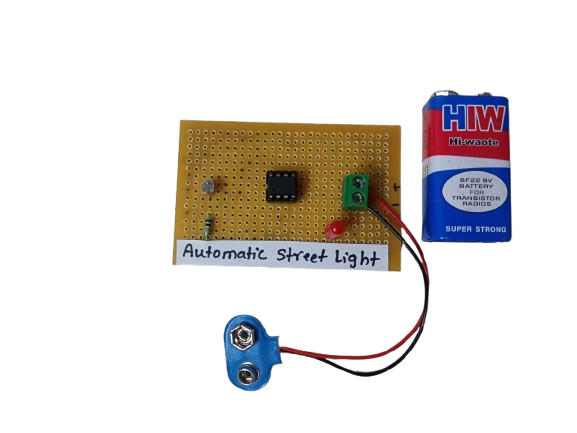
Heartbeat Detector
₹450.00
In StockA heartbeat detector is an essential device for monitoring heart health, providing real-time data about a person’s pulse rate. Whether in a hospital, gym, or a DIY electronics project, it demonstrates how biomedical signals can be measured and processed using sensors and electronics. It’s a valuable tool for both personal health awareness and professional medical diagnostics.
Description
A heartbeat detector is a biomedical instrument that plays a crucial role in health monitoring systems, used to measure a person’s pulse rate non-invasively. These devices are designed to detect the small physical or optical changes in the body caused by the rhythmic contraction and expansion of the heart.
The most common method uses a pulse sensor with a photoplethysmography (PPG) principle:
- An infrared (IR) LED shines light into the skin.
- A photodetector (photodiode or phototransistor) measures how much light is absorbed or reflected, which changes with blood volume.
- Each pulse causes a small fluctuation in the signal, which is processed using filters and amplifiers to detect heartbeats.
Other methods use piezo sensors that detect pressure changes in the arteries, or even ECG electrodes for higher accuracy.
Heartbeat detectors can be standalone devices or part of larger systems, such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, or patient monitoring systems.
-
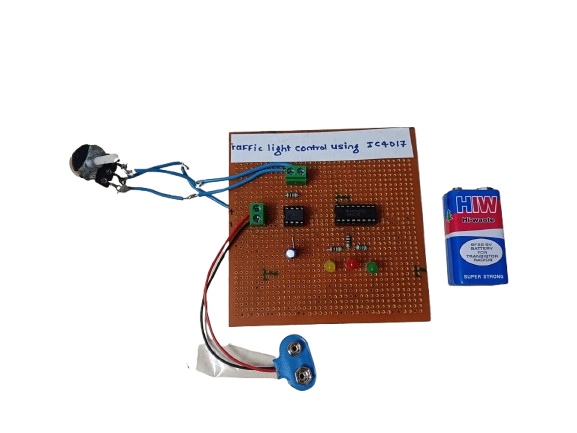
A traffic light control circuit using IC CD4017 is a simple digital electronics project that mimics the working of a real traffic light system. It uses the CD4017 decade counter IC along with a timer (usually 555 IC) to sequentially switch Red, Yellow, and Green LEDs, simulating the flow of traffic signals.
₹250.00 -
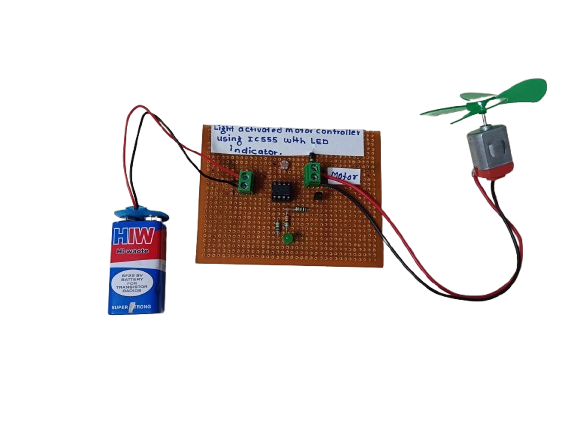
A Light Activated Motor Controller using IC 555 is a simple electronic circuit that turns a motor ON or OFF based on the presence or absence of light. It uses a LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) as a light sensor and the 555 timer IC in a comparator mode, along with an LED to indicate the motor’s status.
₹280.00 -
This project involves controlling a DC motor’s direction using an 8051 microcontroller, with a buzzer and LED indicating the motor’s rotation state. When the DC motor rotates forward, the microcontroller keeps the buzzer and LED off. However, when the motor is rotated in reverse, the microcontroller triggers both the buzzer and LED to turn on as a visual and audible indication of the motor’s reverse rotation