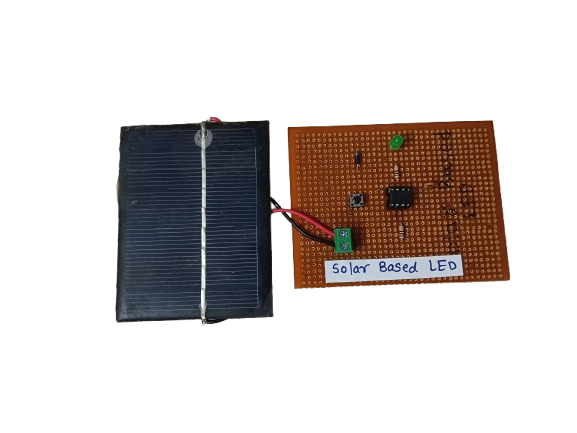
Solar Based LED Lighting System
₹250.00
In StockA solar-based LED system is a lighting setup that uses solar energy to power LED (Light Emitting Diode) lights. During the day, a solar panel captures sunlight and converts it into electrical energy, which is stored in a battery. At night or in low-light conditions, this stored energy powers the LED light.
These systems are eco-friendly, cost-effective, and ideal for off-grid or outdoor applications like street lighting, garden lights, and emergency lighting.
Description
A solar-based LED lighting system combines two modern technologies: solar photovoltaic energy and LED lighting. It is a self-sustaining lighting solution that reduces reliance on grid electricity and promotes the use of renewable energy.
The system typically includes:
- A solar panel to collect sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
- A rechargeable battery (usually lithium-ion or lead-acid) to store the energy.
- An LED lamp, known for its low power consumption, long lifespan, and high efficiency.
- A charge controller to regulate the flow of electricity between the panel, battery, and LED light.
When sunlight is available, the solar panel charges the battery. At night or during cloudy weather, the LED lamp draws power from the battery to provide illumination. Many systems also include automatic dusk-to-dawn sensors, which turn the light on/off based on ambient light levels.
Solar-powered LEDs are especially useful in remote areas where grid power is unavailable or unreliable. They offer a sustainable, low-maintenance, and energy-efficient alternative to traditional lighting systems.